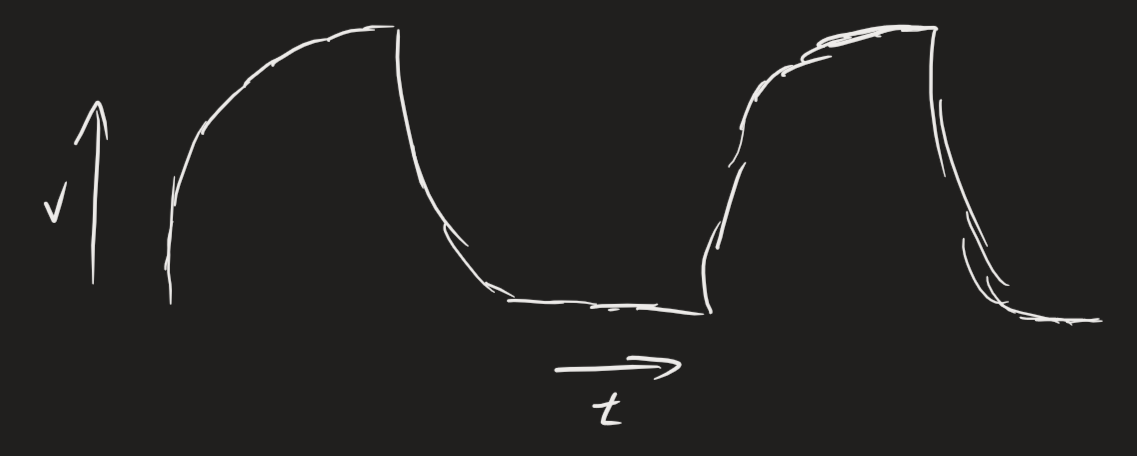
In digital systems, a clock is a periodic signal that oscillates between a high and low state with a constant frequency (roughly in a square wave shape). Clocks are important tools in digital circuit design — and many components, like flip-flops or latches rely on the positive or negative edge of a clock signal to function. In a processor, all registers and components are connected to the clock.
On each edge, the signal should ideally look like a discharging RC circuit when zoomed in. Usually a 5 ns rise time is typical for many digital components used in modern PCB design. This is largely limited by the output capacitance of the transistors used. Obviously, the period cannot be less than the rise time.
Signals are created with crystal oscillators.