As with other logic elements, there’s timing analysis associated with computer memory. Asynchronous memory refers to no clock and no flip-flops on input or output.
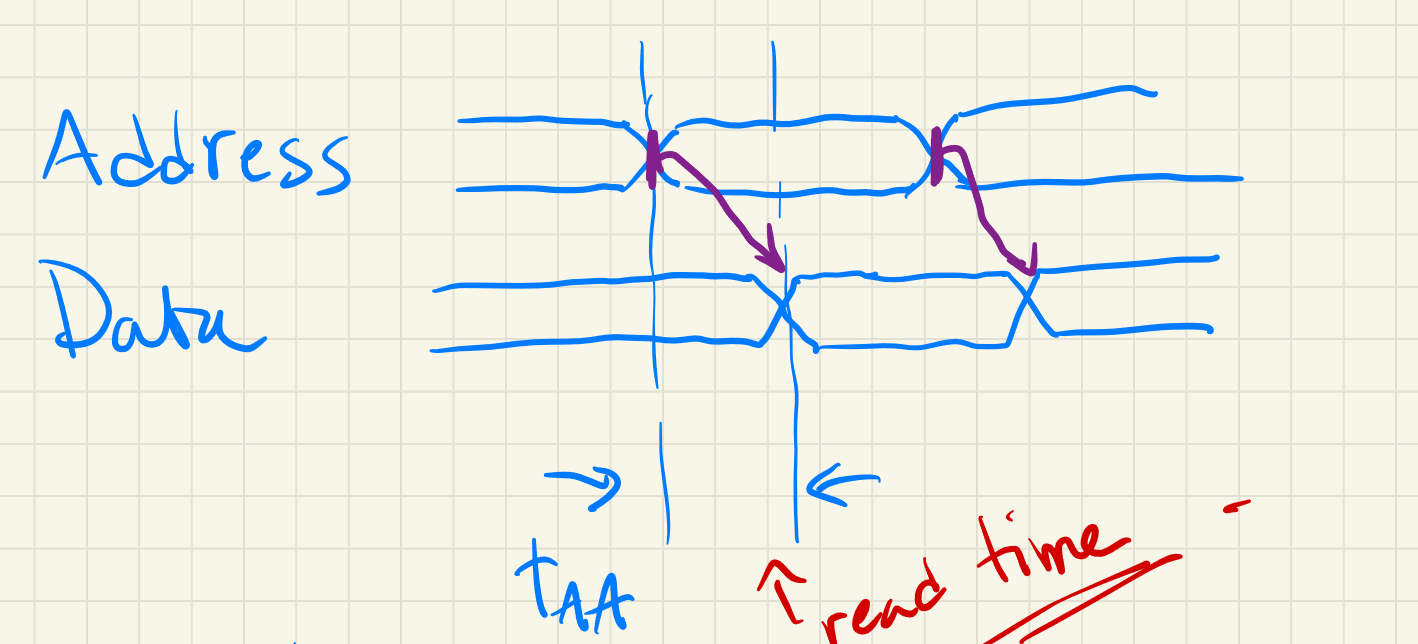
The address access time refers to the amount of time after the address (of the array cell) changes that new data is output.1
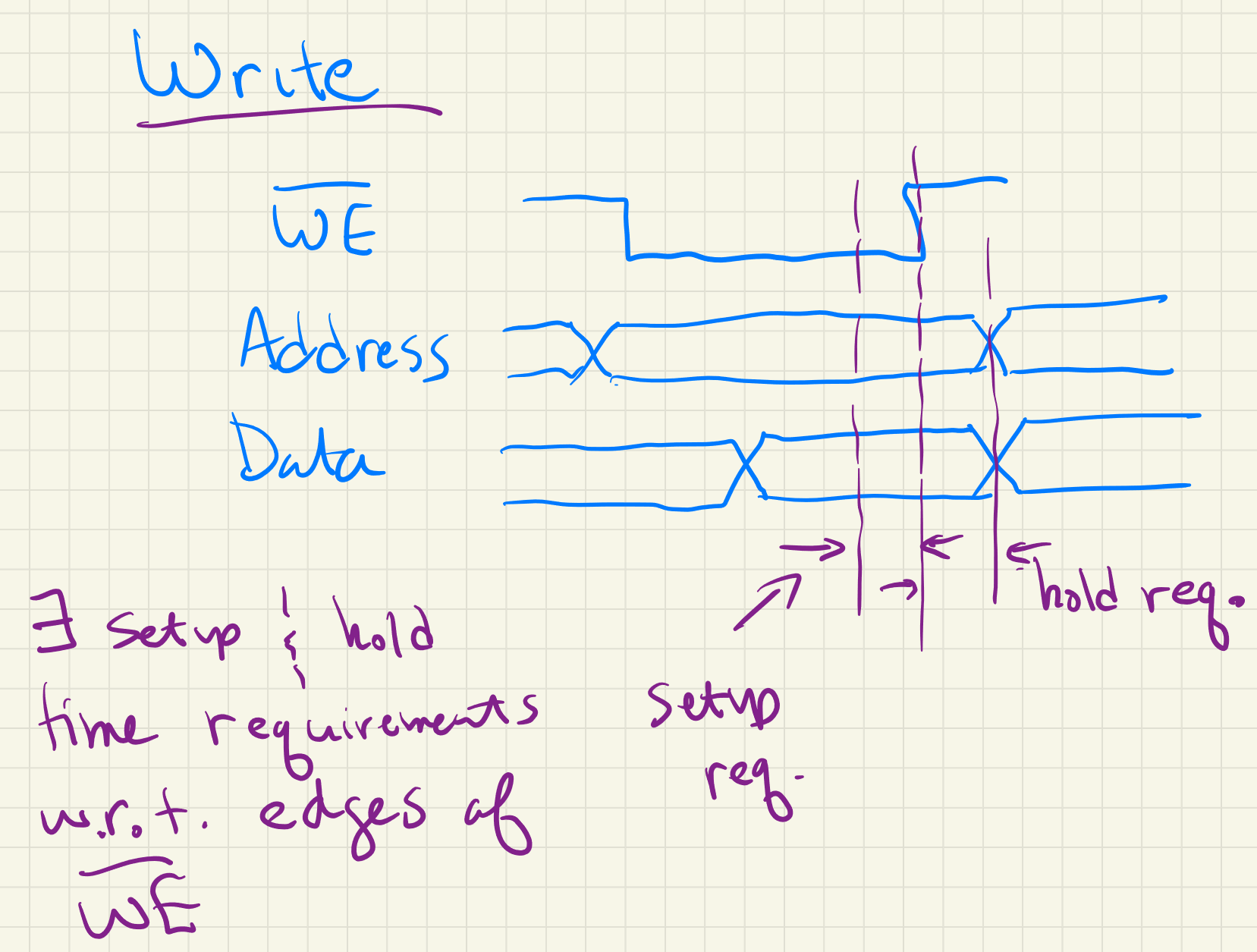
 There are also timing setup and hold requirements associated with the “write enable” signal.
There are also timing setup and hold requirements associated with the “write enable” signal.
Footnotes
-
From Prof Anderson’s lecture notes. ↩