Course focuses on the physics of light, optics, and photonics. Spiritually follows ECE221 — Electric and Magnetic Fields. We cover geometric optics and wave optics.
Very cool course! But super trippy.
Concepts covered
Geometric optics
- Fundamental laws
- Rectilinear propagation
- Law of reflection
- Snell’s law (law of refraction)
- Physical parameters
- Fermat’s principle
- Optical imaging system
- Spherical interface
- Thin lens, Lensmakers’ formula
- Spherical mirror
- Gaussian formula
- Practical imaging systems
- System parameters
- Cardinal points
- Matrix optics
Wave optics
- Wave
- Poynting’s theorem
- Intensity (irradiance)
- Wave polarisation
- Optical boundary conditions
- Interference
- Coherence (temporal, spatial)
- Interferometers
- Resolving power
- Finesse
- Diffraction and Fourier optics
Extra notes
Final
Basic formulas:
Conversions for temporal coherence:
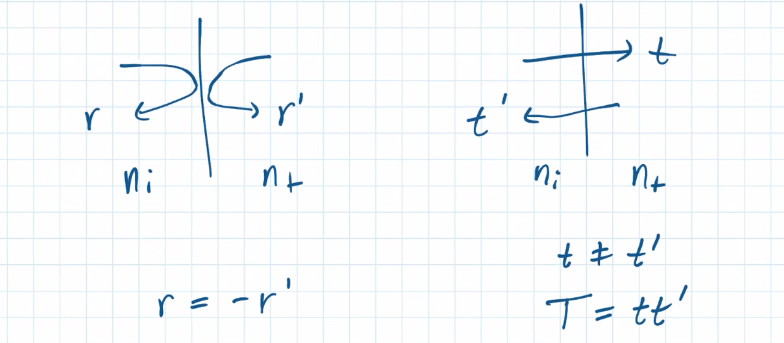 Fringe width (multi-slit diffraction):
Fringe width (multi-slit diffraction):
Midterm III
Polarisation:
- for linear polarisation.
- for angle of polarisation.
- and for circular polarisation.
- Describe magnitude of polarisation.
- Elliptical polarisation otherwise.
- Describe magnitude.
- , if circular/elliptical, then:
- Positive is left-hand polarised
- Negative is right-hand polarised
General waveplates with slow-axis aligned along degree 0 (QWP, HWP):
Fresnel coefficients:
- External reflection:
- Internal reflection: , i.e., is in the denser medium.
For any two dielectric interfaces:
TIR conditions:
- , i.e., the incident light wave is in the denser medium.
- , i.e., the incident angle is greater than the critical angle.
- Brewster angle:
TIR:
- OPL phase change: . Then
Interference conditions:
- non-orthogonally polarised
- constant
Interference:
- Bright fringes:
- Dark fringes:
Conversions for temporal coherence:
Midterm II
Matrix optics:
- Computations should usually be with respect to effective distance.
- Nodal points: special points where ray passing through will exit with same angle.
- Principal point: point that effective distances are wrt to.
Constants:
Units:
- in
- in
- in . If , propagation in positive direction.
- in metres.
- in radians per second.
- is in radians.
Conversions:
Poynting vector:
Polarisation:
- for linear polarisation.
- for angle of polarisation.
- and for circular polarisation.
- Describe magnitude of polarisation.
- Elliptical polarisation otherwise.
- Describe magnitude.
- , if circular/elliptical, then:
- Positive is left-hand polarised
- Negative is right-hand polarised