The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) allows devices to determine an interface’s MAC address if it knows its IP address. Each IP node on the LAN maintains an ARP table that stores a tuple: IP address, MAC address, and TTL. The TTL indicates the time after which an address mapping will be forgotten.
Specification
A typical ARP message is 28 bytes. The protocol message is as follows:
- HW type: 1 for Ethernet.
- Protocol type:
0x800for Internet Protocol. - Operation: 1 for ARP request. 2 for ARP reply.
- HLEN: hardware address length.
- PLEN: protocol address length.
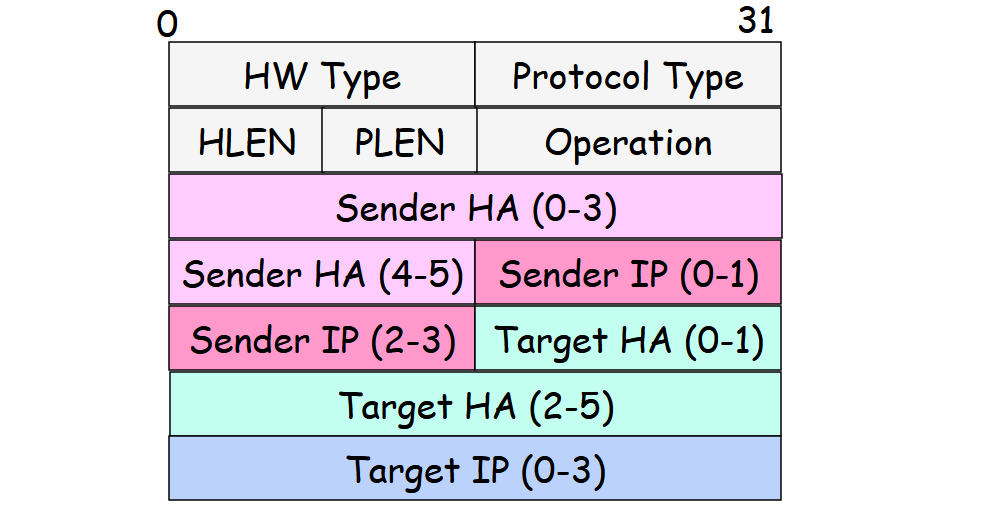 Over Ethernet, it’s given by:
Over Ethernet, it’s given by:

Operation
Suppose we have node A sending a datagram to node B.
- Node B’s MAC address isn’t in node A’s ARP table.
- A uses ARP to find B’s MAC address. It broadcasts an ARP query containing B’s IP address to all nodes in the LAN.
- B replies to A with an ARP response, giving its MAC address.
- A receives this reply, and adds B’s entry into its local ARP table.
If B is on another subnet, then things are different. Assume A knows B’s IP address, A knows the IP address of the first hop router R, and A knows R’s MAC address.
- A creates an IP datagram with IP source A, destination B.
- A creates a link-layer frame containing the IP datagram. R’s MAC address is the frame’s destination.
- A sends the frame to R. The datagram is removed and passed up to IP.
- R determines the outgoing interface, passes the datagram with IP source A, destination B to the link layer.
- R creates the link layer frame containing the A-to-B IP datagram with frame destination B’s MAC address.
- Transmits the link layer frame, which is received by B, and extracted up.
Cache
We can view our machine’s ARP cache with arp -a (on Windows, macOS, and Linux). It has three columns, all of which are quite self-explanatory:
- Internet Address is the IPv4 address of a device on the local network.
- Physical Address is the MAC address mapping.
- Type indicates how the ARP entry was created.
dynamicindicates that the entry was learned through network traffic and will expire after a timeout.staticindicates that the entry was manually configured and won’t expire until the computer restarts or the entry is manually removed.
Resources
- ARP specification by Gorry Fairhurst