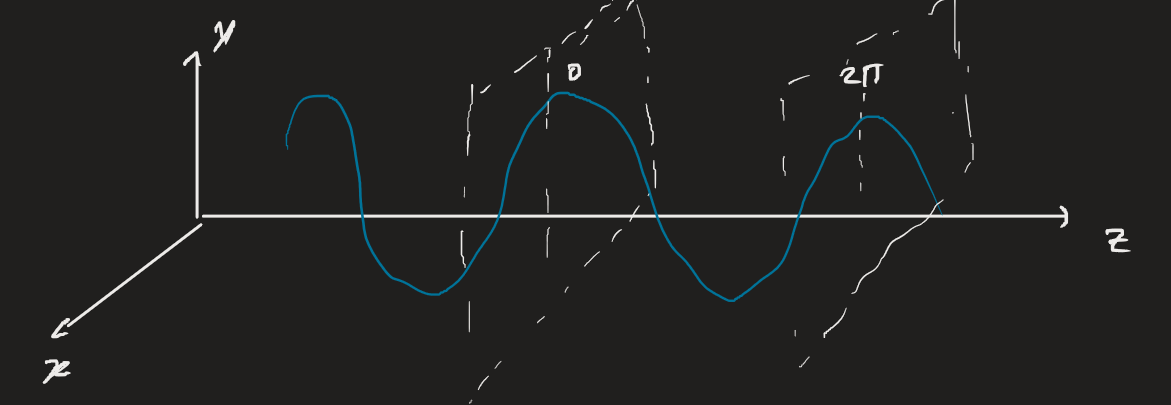
A harmonic wave (or monochromatic wave) is a single-frequency wave. It varies according to a sinusoid in both time and space. If we fix space and observe oscillation, we get a temporal frequency and period. If we fix time and observe, we get a spatial frequency and period.
A plane wave propagates such that the field is uniform over every plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation. All points with the same form a plane perpendicular to .
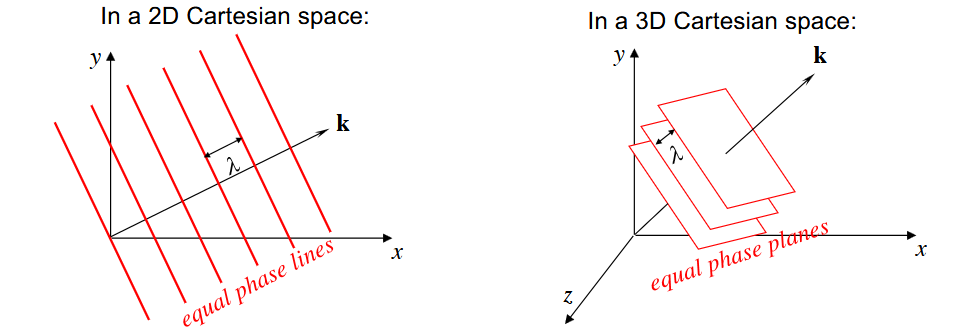 The general form of a harmonic plane wave in Cartesian space is:
The general form of a harmonic plane wave in Cartesian space is:
where we have the parameters:
- is the amplitude of oscillation. Its vector direction is the polarisation direction. Units are in volts per metre (same as regular electric field).
- indicates the propagation direction. For (above), this indicates propagation in the positive direction. For , it indicates the negative direction. Units are radians per metre.
- is the position vector in metres.
- indicates the spatial frequency.
- indicates the temporal frequency, in radians per second.
- And is the initial phase at , in radians.
In isotropic media, plane waves are transverse: and .