A data structure is a way to store and organise data. Our choice of what data structure to use is important — because it may change the runtime complexity of basic operations, like searching, inserting, and deleting nodes.
We implement data structures in classes in most languages. In some languages, like C/C++, we may use the struct type to implement data structures.
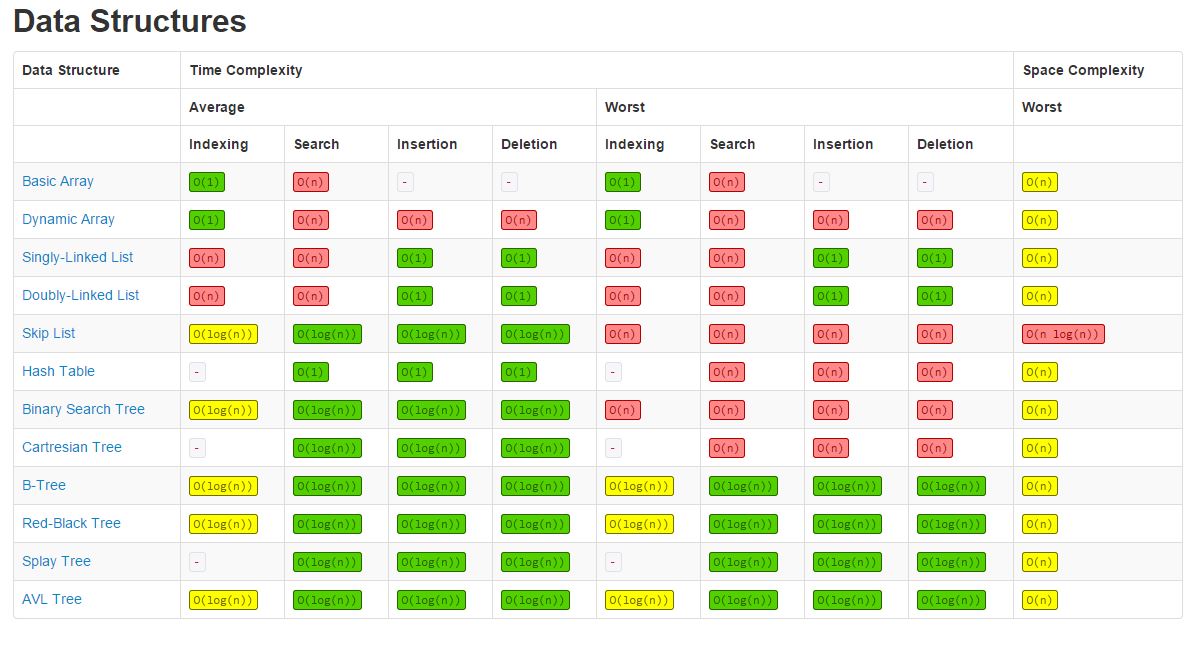
Basic operations
Often we are interested in the implementation and space/time complexity of a few basic operations:
- Searching through the structure for a certain value
- Inserting data, perhaps depending on a sorting condition
- Deleting a node with particular data or the structure
- Copying the structure from one to another
While writing functions for these operations, consider:
- Will they work if the structure is empty?
- Will they work if the data is not in the list?
- Will they work if we need to work regardless of the position?
- If at the end, set next pointer to null.
- If at the head, change the head pointer.
- If in the middle, ensure pointers behind and in front are properly updated.
Sub-pages
Courses
- APS105 — Computer Fundamentals
- ECE244 — Programming Fundamentals
- ECE297 — Software Design and Communication
- ECE345 — Algorithms and Data Structures
Resources
- Introduction to Algorithms, by Thomas Cormen, Charles Leiserson, Ronald Rivest, Clifford Stein (CLRS)
- Data Structures and Algorithms in {Java, C++, Python}, by Michael Goodrich and Roberto Tamassia