The magnetic field () is a vector field, generated by a current-carrying wire at a position in space. The magnetic flux density () is measured in teslas (), proportional to the magnetic field intensity.
where is the permeability constant of the medium.
We can compute the magnetic field and flux density using the Biot-Savart law or Ampere’s law (where there’s symmetry).
Properties
A fundamental postulate of magnetism is that magnetic flux lines are always closed. From the below relations for the divergence/curl of a magnetic field, we conclude that there’s no magnetic point source (the same way there is for electric charge). We cannot isolate a magnetic monopole, so a material will function as a source and sink and not either; magnets only exist as dipoles.
Gauss’ law for magnetism states that:
Ampère’s law states that:
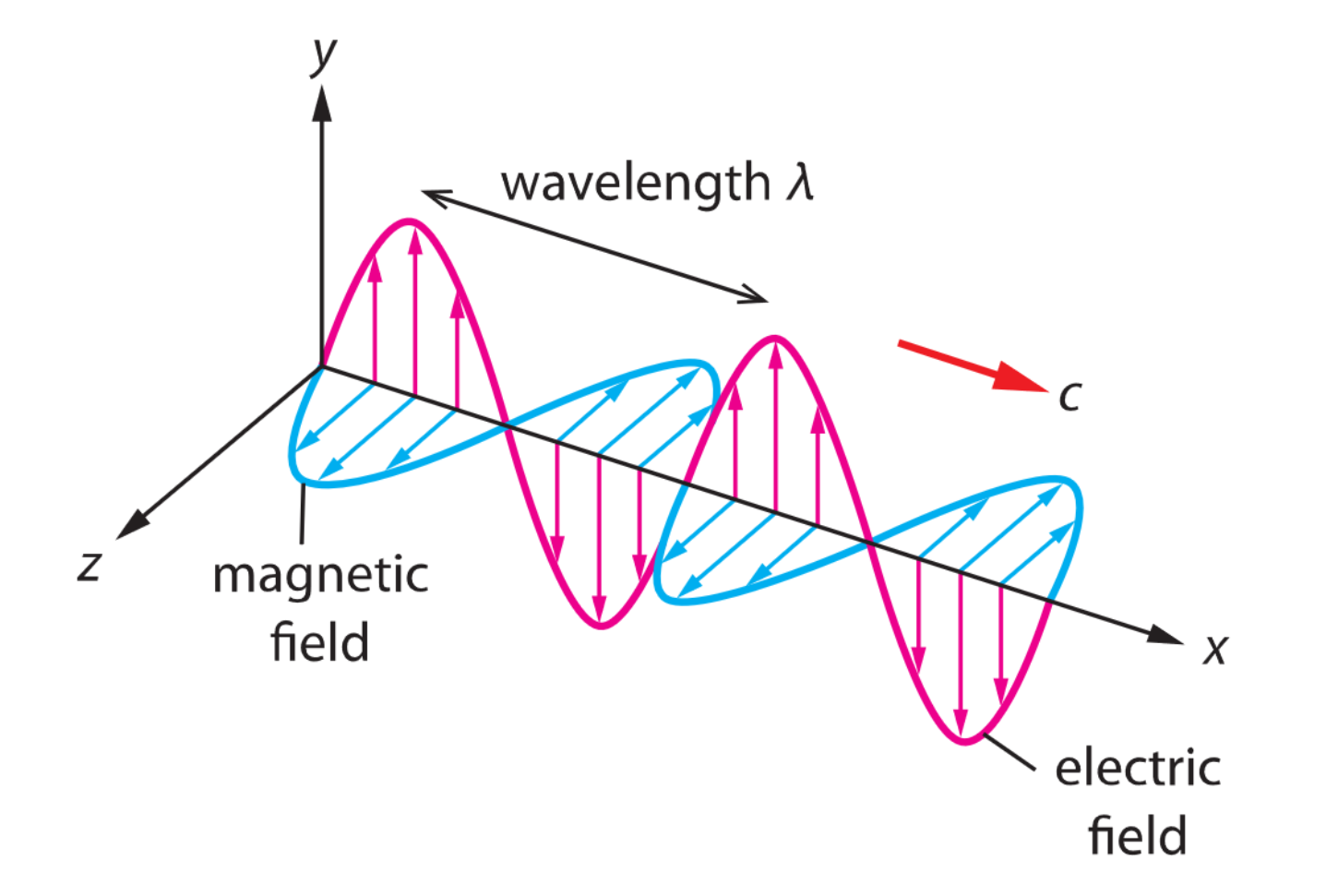
An oscillating electric field produces a perpendicular oscillating magnetic field, both at the speed of light in a vacuum. They’re collectively called electromagnetic waves, and are transverse waves.