Doping is the practice of adding impurities (dopants) to semiconductors to control their electrical conductivity. If we add extra electrons, we call them n-type semiconductors and if we remove electrons (add extra holes), we call them p-type semiconductors (both for negative and positive).
N-type
Remember that silicon has 4 valence electrons, To create n-type compounds, we add phosphorous, since it carries extra electrons (to the right on the periodic table).1
![]() The extra electron is weakly bound and can be easily promoted. For this reason, we say that it has an extra donor energy level within the band gap.
The extra electron is weakly bound and can be easily promoted. For this reason, we say that it has an extra donor energy level within the band gap.
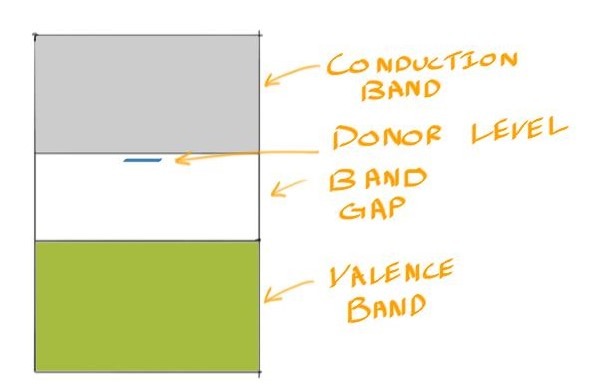 N-types have a conductivity given by:
N-types have a conductivity given by:
P-types
We dope with boron to create extra holes. This means we can promote electrons into the extra hole for every dopant atom.
![]() Just as n-types have a donor level, p-types have an acceptor level in their band gap near the valence band.
Just as n-types have a donor level, p-types have an acceptor level in their band gap near the valence band.
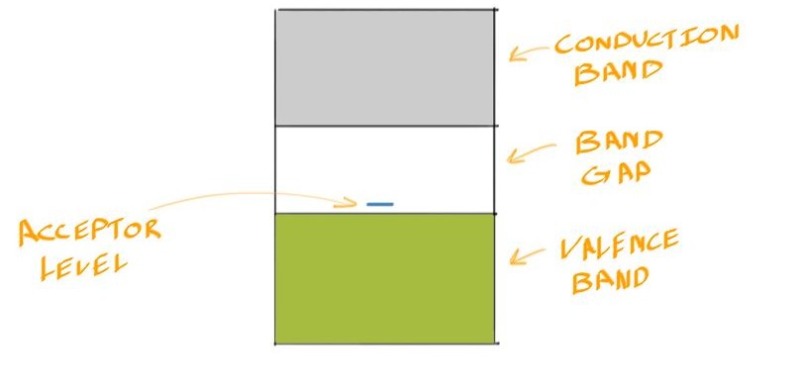 And its conductivity is given by:
And its conductivity is given by:
Footnotes
-
From Engineering Chemistry and Materials Science, by Scott Ramsay. ↩