In graph theory, the shortest path problem finds a path between two vertices such that the weight of its edges is minimised. A few definitions:
- The problem operates on a weighted, directed graph .
- A weight function maps edges to weights, .
- The weight of path is the sum of the weights of each constituent edge from vertices .
The shortest path is given by the smallest weight, i.e., the shortest-path weight from to is defined as:
What possible applications does this have?
- Mapping software direction planning
- FPGA routing
- Integrated circuit gate connections
- Internetworking, to deliver information from one computer to another
Some shortest path algorithms include:
Variations
SSSP — single source to all vertices SDSP — single destination from all vertices reverse of SSSP single pair shortest path — from vertex to all pair — self explanatory we can use SSSP to solve all variants
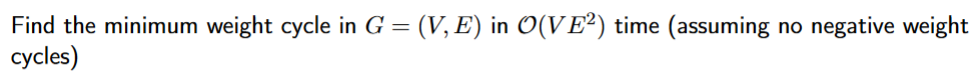 bellman ford for each edge
bellman ford for each edge
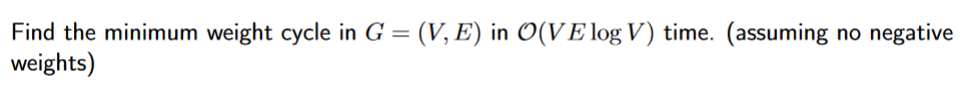 dijkstra’s for each vertex, store in matrix
lookup matrix, s(u, v) + s(v, u) ⇒ take smallest
dijkstra’s for each vertex, store in matrix
lookup matrix, s(u, v) + s(v, u) ⇒ take smallest
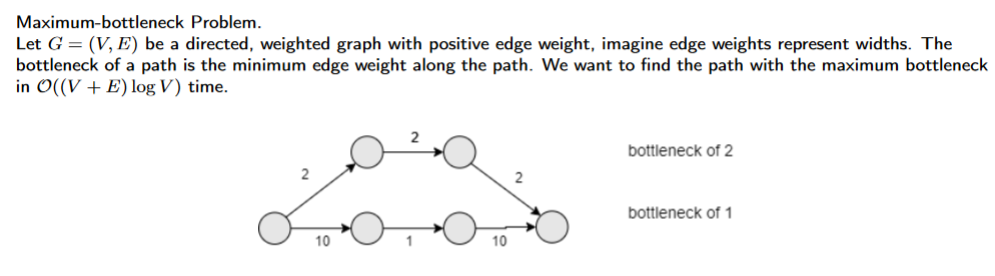 dijkstra but we modify the relax function
s -p→ u → v; either bottleneck is in p or in new edge (u, v)
dijkstra but we modify the relax function
s -p→ u → v; either bottleneck is in p or in new edge (u, v)
relax(u, v, w)
if (v.d < min(u.d, w(u, v)))
v.d = min(u.d, w(u, v))
v.pi = uwe initialise source with , initialise everything else with 0
Applications
In Internetworking
Routing algorithms are used in the network layer’s control plane. Their goal is essentially to find “good” paths from sending hosts to receiving hosts, through a network of routers, which is abstracted as a graph.
There are many types of routing algorithms:
- How much information does each router have?
- Global information means all routers have information of the complete topology and link cost information. These are called link state algorithms (like Dijkstra’s).
- Decentralised information means there’s an iterative distributed process of computation where information is exchanged with neighbours. Routers initially only know link costs to attached neighbours. These are called distance vector algorithms (like Bellman-Ford).
- What is the timescale that these algorithms iterate? i.e., that these paths change?
- Static means routes change slowly over time.
- Dynamic means routes change more quickly, with periodic updates or in response to link cost changes.

Link-state algorithms are generally preferred. This is because of:
- Fast, loopless convergence.
- Less routing information for transmission to neighbour nodes. Usually the number of links is much smaller than the number of networks.
- Support for precise metrics, and multiple metrics (throughput, delay, cost, reliability) if necessary.
- They also support multiple paths to a destination, i.e., the algorithm can be modified to find the best two paths.