An integrator is a circuit that outputs the integral of an input signal. They’re implemented with a capacitor and operational amplifier. There are two main configurations.
Our first case is the inverting op amp integrator:
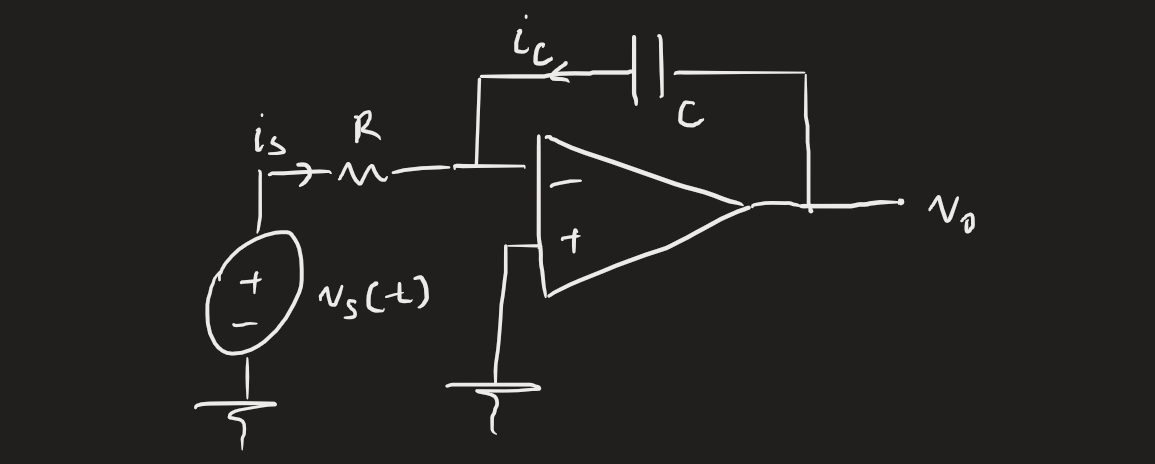 From KCL, we get:
From KCL, we get:
If the capacitor is initially discharged, then , then the output voltage is proportional to the integral of the input voltage.
Alternate configurations
For the non-inverting integrator:
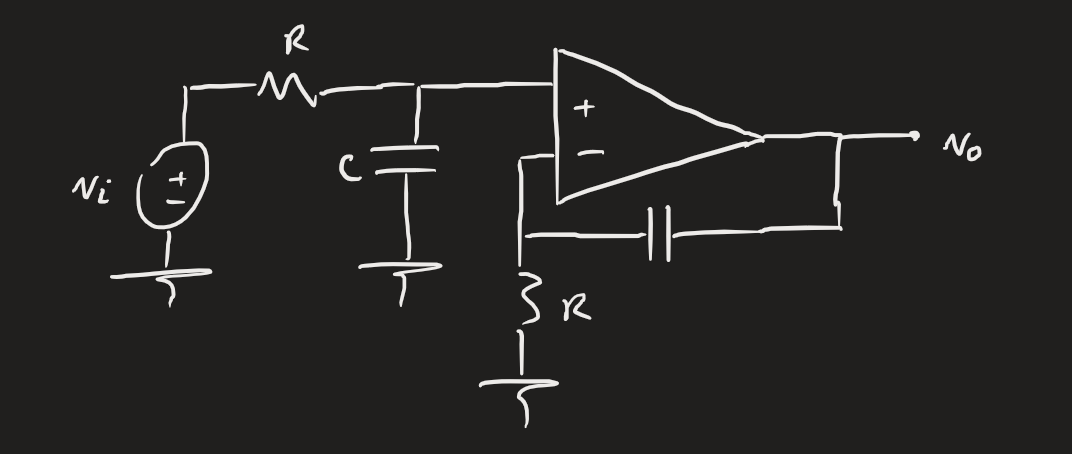 From KCL:
From KCL:
In practice, the inverting configuration requires a large feedback resistor in parallel with the capacitor. This is because any DC/low frequency component may cause the op amp output to saturate otherwise.
Applications
They’re usually used to measure things, like voltages. In a sense, they’re similar to their digital counter equivalent.
Integrators can also be used in conjunction with an oscillator circuit to produce both triangle and square waves simultaneously.