The electromagnetic spectrum describes the range of radiation that exists physically. This covers radio, infrared, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays, and visible light (which is a small subset of the spectrum).
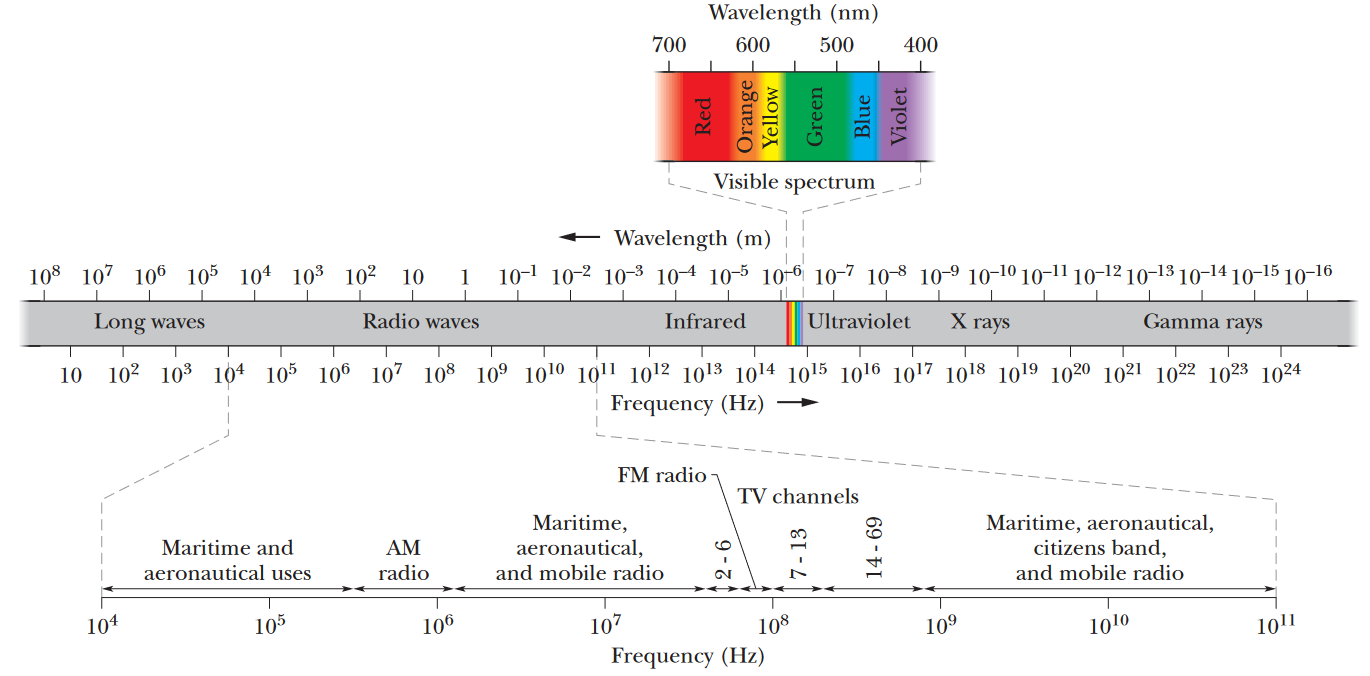 From left to right, we have waves with the longest wavelengths (and lowest energy) to the shortest wavelengths (and highest energy).
From left to right, we have waves with the longest wavelengths (and lowest energy) to the shortest wavelengths (and highest energy).
- Visible light falls between 400 and 700 nm.
Energy in the electromagnetic spectrum is quantised and proportional to its wavelength:
where , Planck’s constant, , the speed of light in a vacuum, and is the wavelength. Alternatively:
where is the frequency of the wave.