The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an IP address allocation protocol. Hosts will dynamically get an address from a network server when it joins the network. It can renew its lease on the address in use, it allows for reuse of addresses (only held while connected), and it supports mobile users who join/leave network.
The DHCP server is typically co-located in the router, and it serves all subnets to which the router is attached. It runs over UDP. The client uses port 68, and the server uses port 67.
More information is needed to configure the host’s connection. So DHCP can return more than just the allocated IP address. It can also allocate:
- The address of the first-hop router for the client.
- Name and IP address of the DNS server.
- Network mask that indicates the network versus host portion of the address.
Communication
The general scheme is:
- host broadcasts DHCP discover message
- DHCP server responds with DHCP offer message
- host requests IP address: DHCP request message
- DHCP server sends address: DHCP ack message
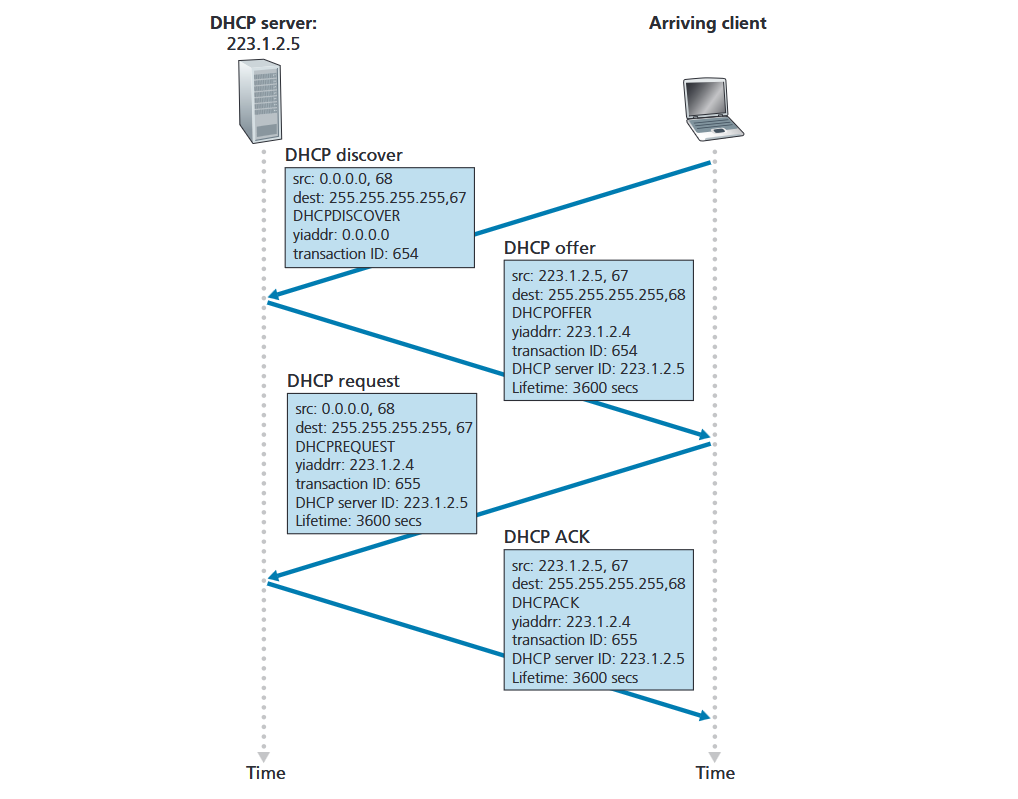
In the request message:
- A transaction ID is used to match the requests. For retransmitted messages, clients may choose to reuse the same transaction ID.
- A lifetime denotes the lease length of the IP address.
The first 2 messages are optional. If the client remembers and wishes to reuse a previously allocated address, then it can directly use the host address packets (last 2 messages).