Newton’s laws of motion are key to analysis in statics and dynamics.
First law
A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line with constant velocity, tends to remain in this state provided the particle is not subjected to an unbalanced force.
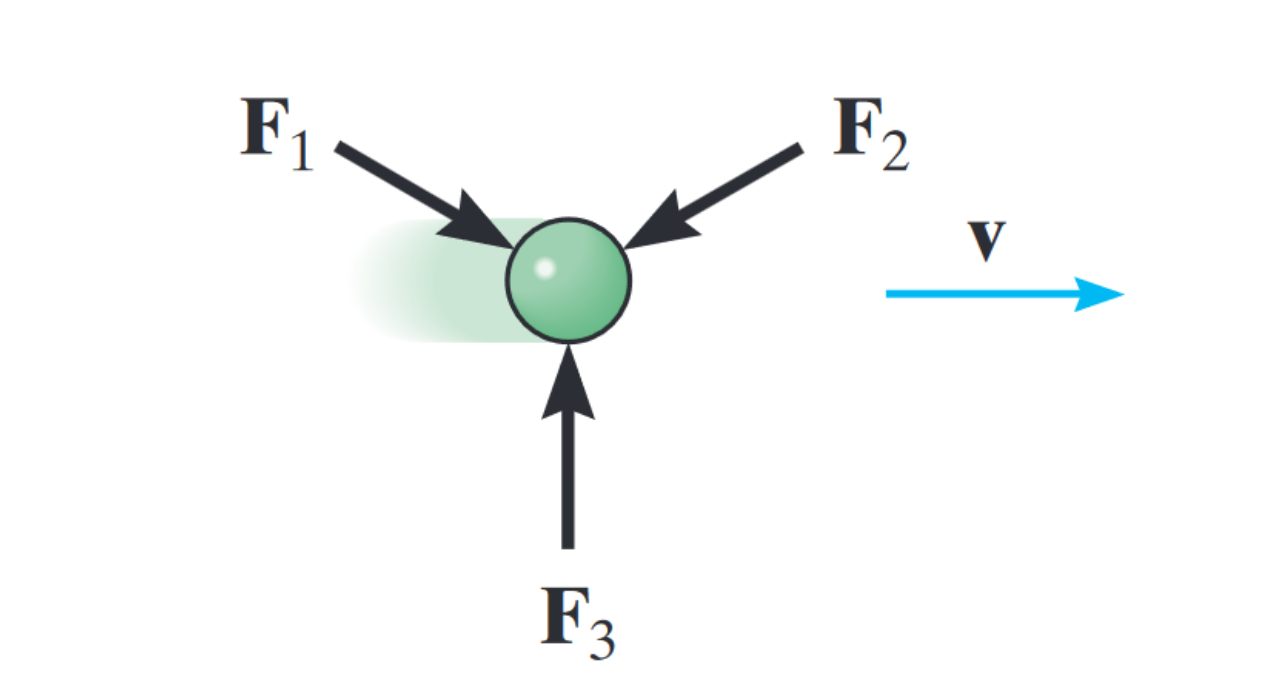
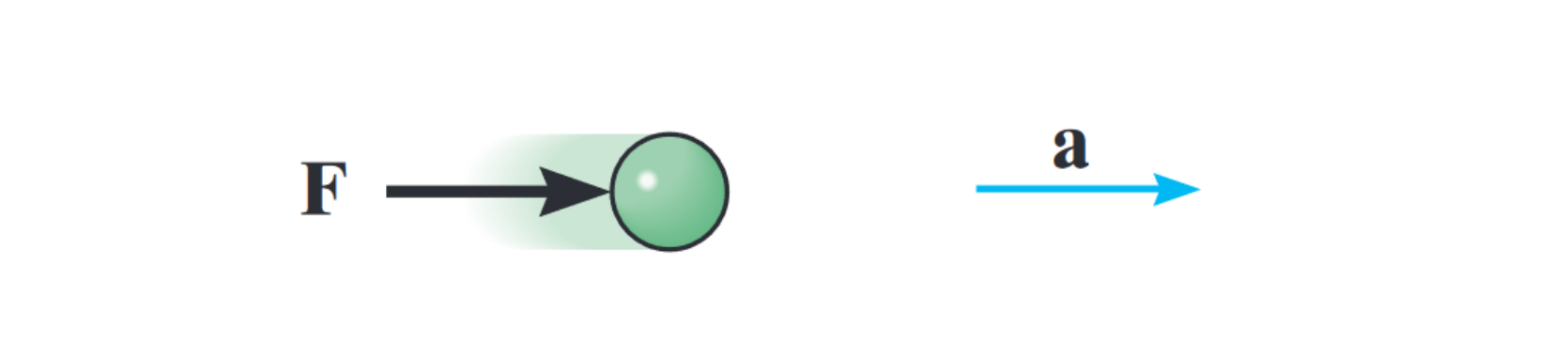
Second law
The acceleration of a particle is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and is in the direction of this force, expressed as:
Especially foundational for force kinetics analysis.
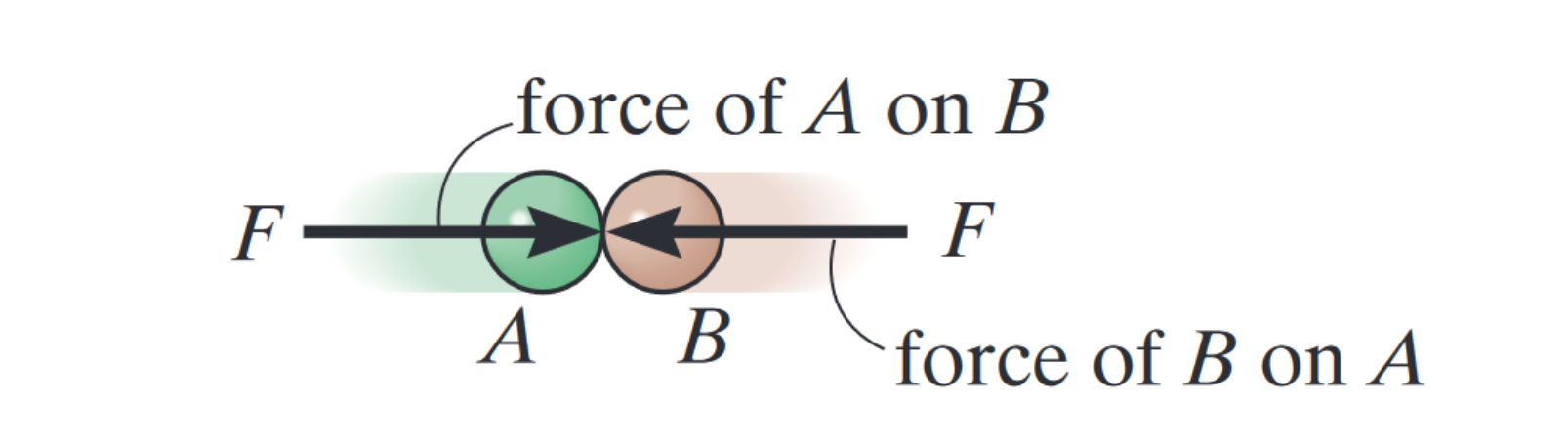
Third law
The mutual forces of action and reaction between interacting bodies are equal in magnitude, opposite, and co-linear.