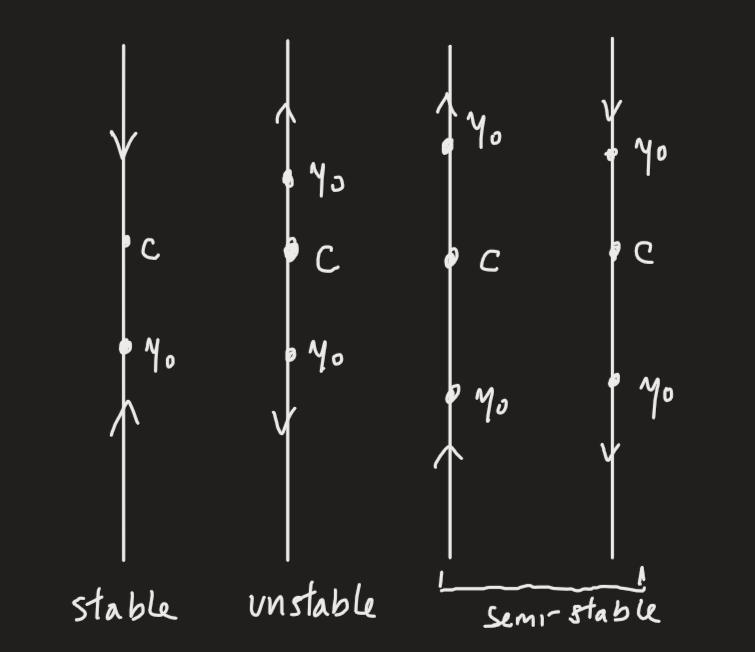
A constant solution of a differential equation such that the rate of change is equal to 0 is called an equilibrium solution (sometimes called critical points). We have three types of equilibria solutions:
- Steady-state (or asymptotically stable), where the rate of change approaches the solution from both sides
- Semi-stable, where the rate of change approaches the solution from only one side
- Unstable, where the rate of change actively goes the opposite direction from both sides
In text, this is hard to visualise. Consider this phase portrait, with steady-state (a), unstable (b), and semi-stable (c-d) below: