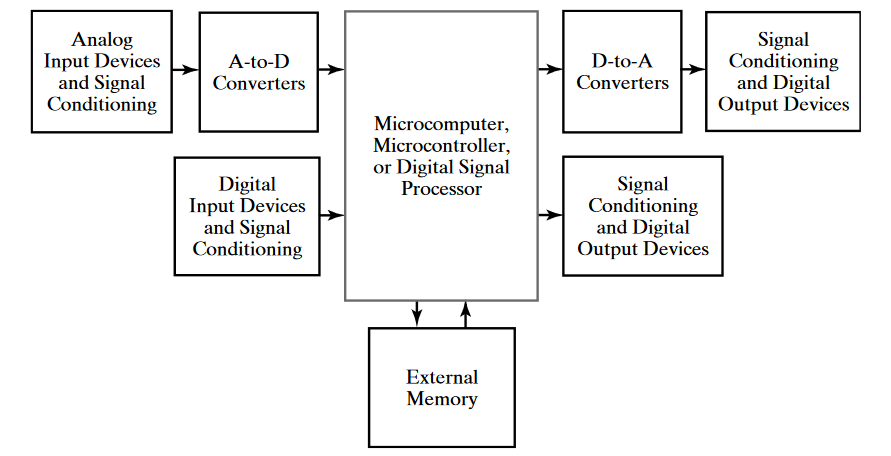
Embedded systems are computers that are integrated into a larger device or system. At the core of embedded systems are microcomputers (which often contain microcontrollers). The software that runs on embedded systems are often permanently stored to provide only the required functionality of the product, called embedded software.
Embedded software is often written in C or Rust, primarily due to limited memory requirements and a lack of compilers for other languages.
Tools
Languages
Hardware
Resources
See also
C is a common language for embedded systems, because of its broad compiler support and being lightweight on memory.
The volatile specifier tells the compiler not to optimise anything associated with the variable. There are a few important use cases of this, including when we interface with hardware that changes the value itself (as opposed to within the program).
In Nios, using
volatiletells the compiler to useldwioandstwioinstructions instead ofldwandstw.
Certain types will map to particular bit lengths. From here, we can effectively interface with any embedded device as flexibly as needed.
intcorresponds to a 32-bit number, so any 32-bit system can store addresses inint.short intcorresponds to a 16-bit number, i.e., a half-word in a 32-bit system.long intcorresponds to a 64-bit number, i.e., a full word in a 64-bit system.charcorresponds to an 8-bit number, i.e., a byte in a 32-bit system.