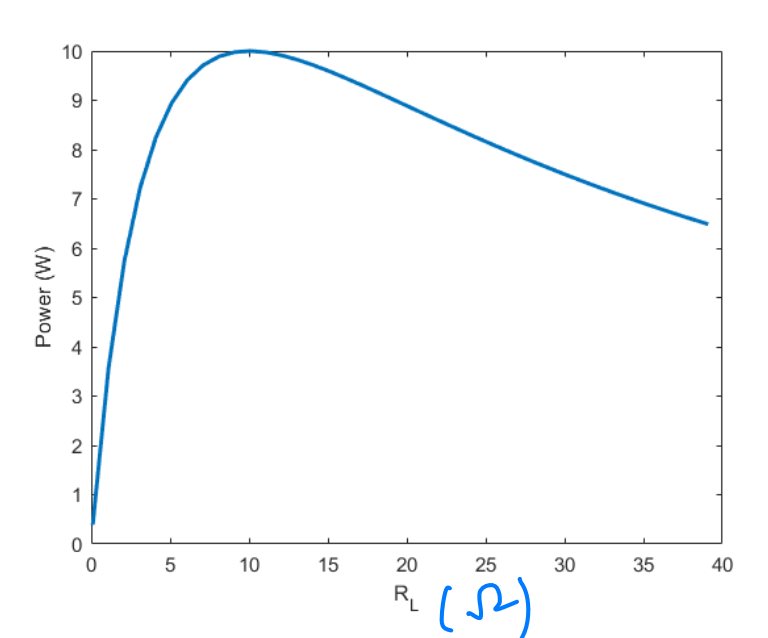
We are sometimes interested in determining the maximum power that can be delivered to some load. This can be determined with Thevenin’s theorem or Norton’s theorem.
In the DC case, power delivered to the load is maximised when the load resistance is equal to the equivalent resistance, i.e., . In the AC case, this is when the impedance is the conjugate of the Thevenin impedance .
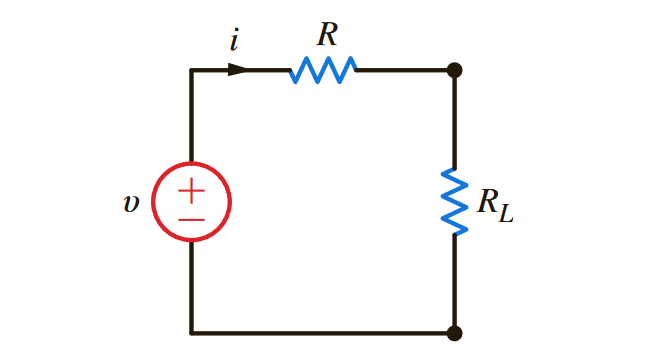 As a result, the power is given by:
As a result, the power is given by:
The derivation
Since power is given by:
We can take the derivative and set to 0 to maximise:
which gets us the above result.